Waves
6 Topics | 5 Quizzes
Electromagnetic Radiation
11 Topics | 10 Quizzes
The Visible Light Spectrum and Colour
8 Topics | 7 Quizzes
Reflection and Mirrors
9 Topics | 8 Quizzes
Refraction and Lenses
10 Topics | 9 Quizzes
Sound Waves
9 Topics | 8 Quizzes
Heat Energy and Heat Transfer
6 Topics | 5 Quizzes
Introduction to Electricity
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
Electric Circuits and Circuit Diagrams
4 Topics | 3 Quizzes
Measuring Electricity – Voltage and Current
8 Topics | 7 Quizzes
Electrical Resistance and Ohm’s Law
7 Topics | 6 Quizzes
6 | Summary

6 | Summary
Summary
- Waves are oscillations that transfer energy.
- Mechanical waves require a medium, which means they can travel through solids, liquids and gases, but not through a vacuum.
- Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium, which means they can travel through solids, liquids and gases, as well as through a vacuum.
- All waves require a source of oscillations.
- Mechanical waves require the disturbance of a medium.
- Electromagnetic waves require a source that generates an oscillating electromagnetic field.
- Transverse waves involve oscillations that are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
- Longitudinal waves involve oscillations that are in line with the direction of energy transfer.
- Surface waves involve oscillations that are circular.
- Frequency is the number of wave cycles per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz).
- Wavelength is the distance a wave travels during one cycle.
- Amplitude is the maximum distance of oscillation from the central starting position.
- Velocity is how fast a wave travels through space.
- Waveforms are graphical representations of waves.
- They show amplitude as the height of peaks and wavelength as the distance between two peaks.
- Frequency, wavelength and velocity are mathematically related, as shown by the following formula:
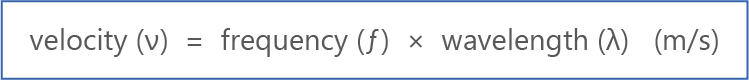 .
.
- Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional.
- Amplitude does not affect frequency, wavelength or velocity.