3 | Chemical Subunits
Chemical Subunits
- Pure substances have fixed properties because they are made up of only one type of chemical subunit.
- A chemical subunit can be defined as the smallest fraction of a pure substance that still has the properties of that substance.
Atoms
- The simplest type of chemical subunit is an atom.
- Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all matter.
- Atoms only rarely exist as individual subunits.
- The only atoms that exist individually are those of the noble gases.
- These are the elements which are located in group 18 of the periodic table. They include helium, neon and argon.
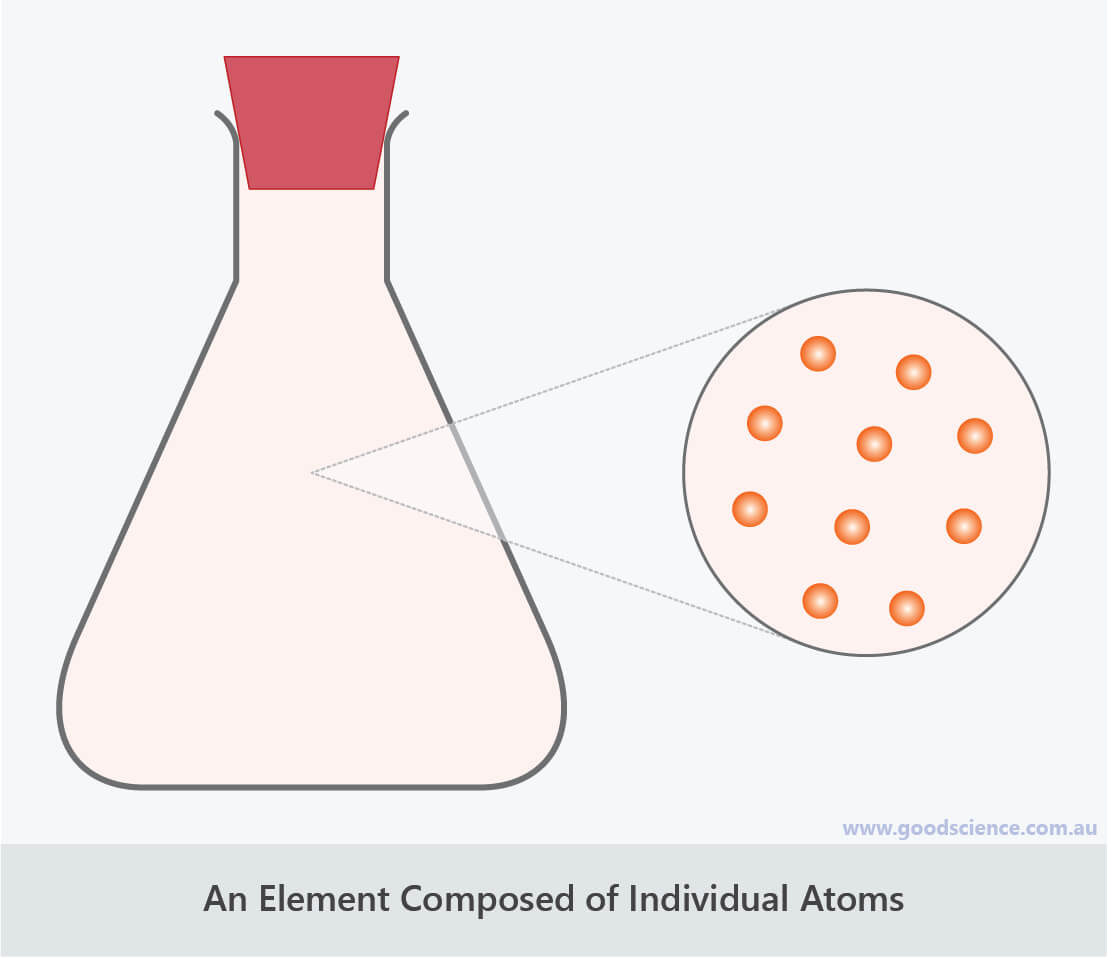
Helium is an example of an element with atoms arranged individually.
- More often, atoms are connected to other atoms by strong forces of attraction known as chemical bonds.
- These bonded atoms can form two types of chemical structures: molecules and lattices.
- Molecules and lattices can consist of one type of atom (and therefore form the subunit of an element), or consist of more than one type of atom (and therefore form the subunit of a compound).
Molecules
- Molecules are discrete chemical subunits consisting of fixed arrangements of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
- Most non-metal elements other than the noble gases have molecules as their subunits.
- These include hydrogen, nitrogen and chlorine.
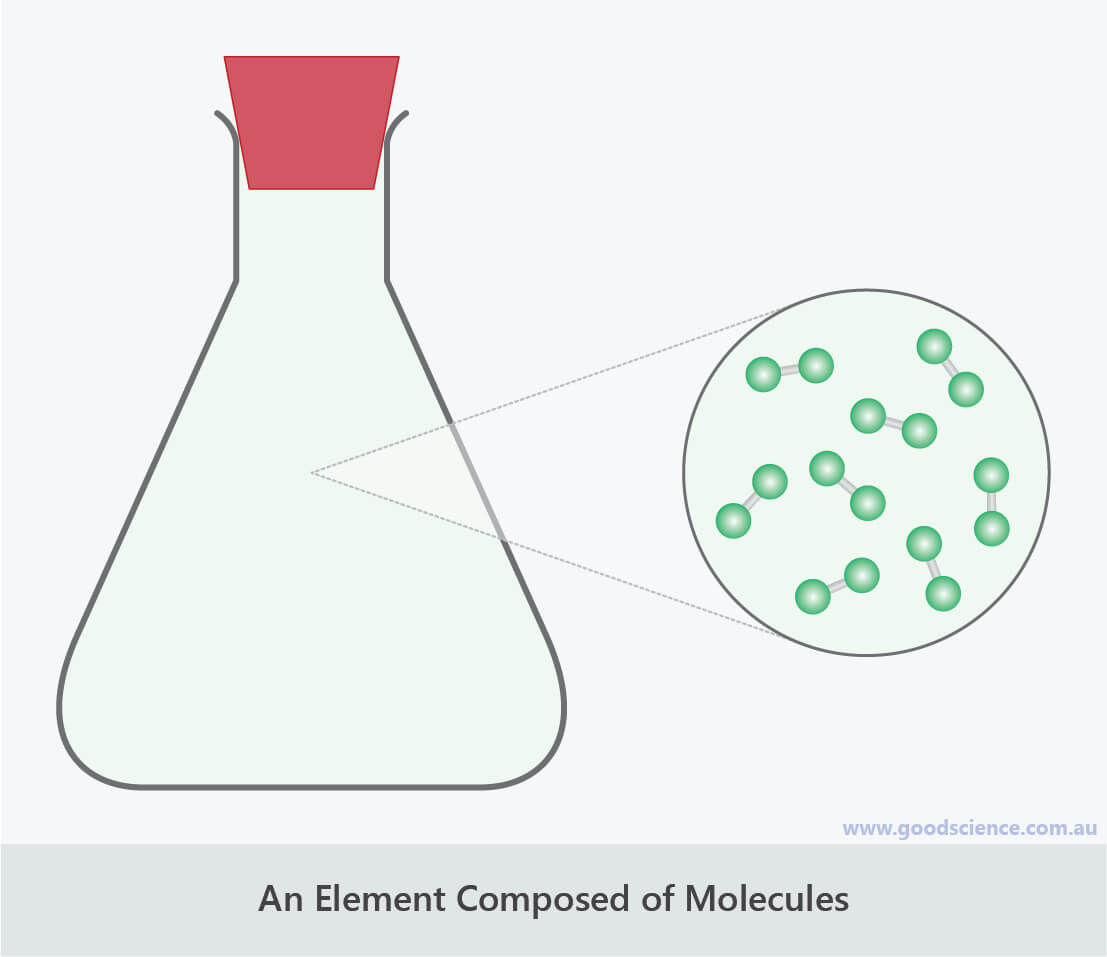
Chlorine is an example of an element with atoms arranged in molecules.
- Most compounds have molecules as their subunits.
- These include small molecules, such as water, carbon dioxide and methane, but also large molecules, such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
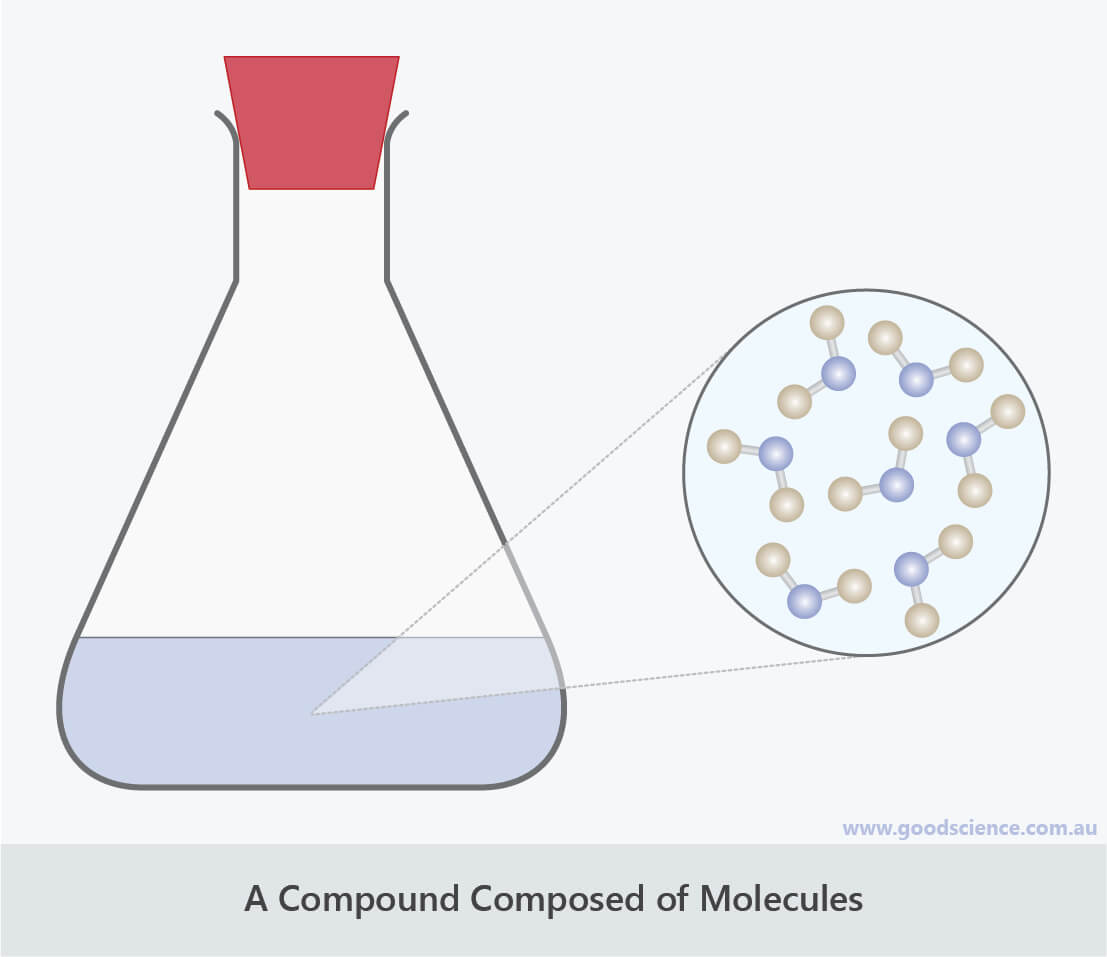
Water is an example of a compound with atoms arranged in molecules.
Lattices
- Lattices are continuous networks of atoms in a fixed arrangement, held together by chemical bonds.
- All metal elements consist of atoms arranged as a lattice.
- Carbon and silicon are two examples of non-metal elements whose atoms are arranged as a lattice.
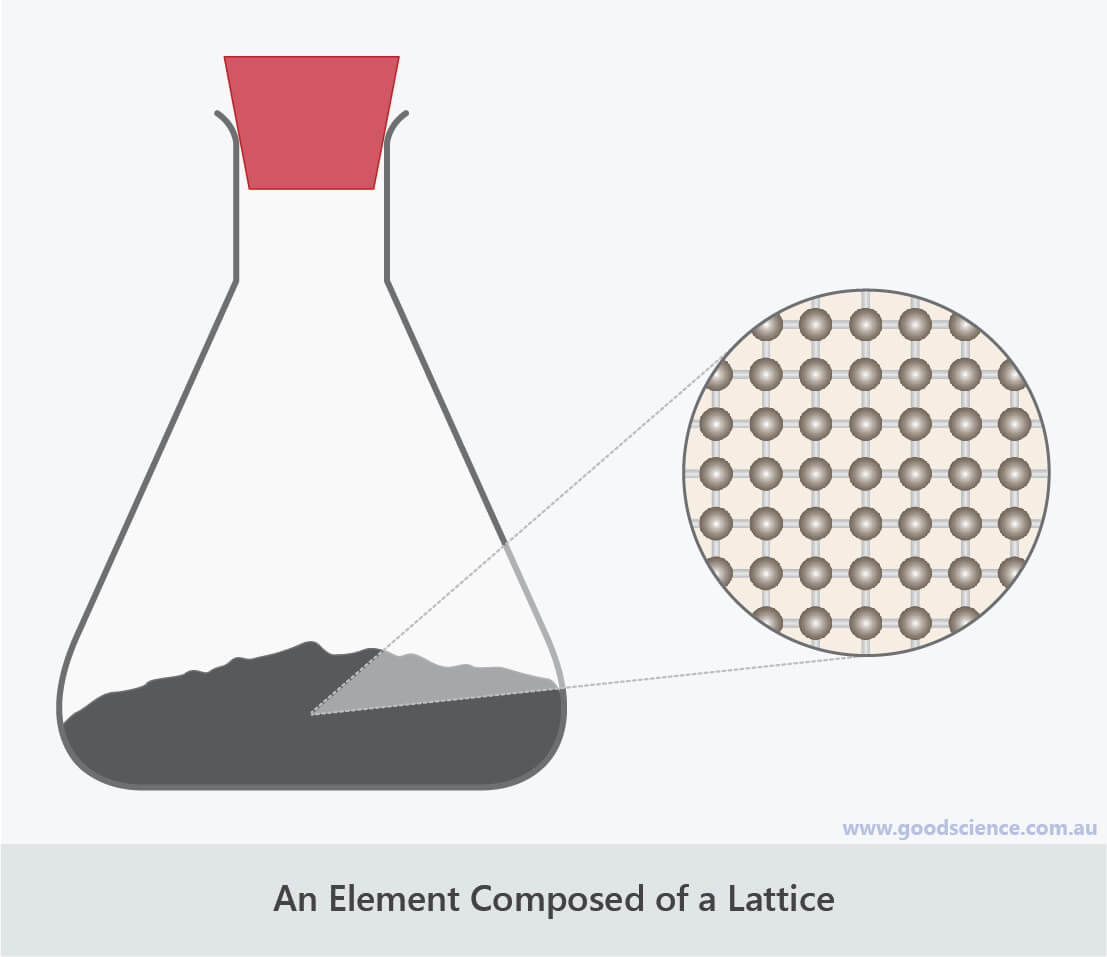
Carbon is an example of an element with atoms arranged in a lattice.
- Silicon dioxide and sodium chloride* are two examples of compounds whose atoms are arranged as a lattice.
- (*Most compounds that exist as lattices – such as sodium chloride – are ionic compounds; therefore, the lattices are actually made up of positive and negative ions rather than atoms. We will learn about ions and ionic compounds later.)
![]()
Silicon dioxide is an example of a compound with atoms arranged in a lattice.
Quizzes

