3 | Other Laboratory Equipment
Bunsen Burner
- A Bunsen burner is a portable gas burner.
- It consists of a narrow vertical metal tube, a flat stand, a gas inlet attached to a rubber hose – which attaches to a gas tap, and an air hole surrounded by an adjustable collar.
- Bunsen burners are used for heating, burning and sterilising materials in a laboratory.
- They are often used in conjunction with a tripod, for example, when heating liquids in a beaker or solids in a crucible.
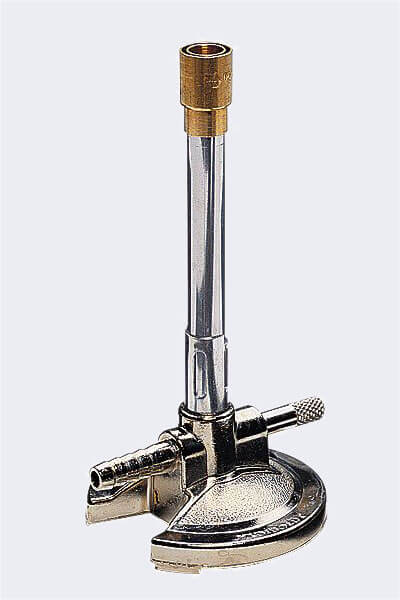

A Bunsen burner
(Image: Polimerek, Wikimedia Commons)
Tripod
- A tripod is a three-legged metal stand with a flat, triangular or round platform.
- Tripods are primarily used for holding objects that are being heated by a Bunsen burner.
- They are placed over the Bunsen burner and objects placed on the tripod.
- When heating substances in a beaker, a wire gauze is placed on the tripod and the beaker is placed on the wire gauze.
- When heating substances in a crucible, a pipeclay triangle is placed on the tripod and the crucible is placed inside the pipeclay triangle.
- Since the top section of a tripod can get very hot during use with a Bunsen burner, the safest way to handle them is by the bottom of the legs, as these don’t get hot.
- Ideally, a tripod should be allowed to cool down before being handled.

A tripod
(Image: NagayaS, Wikimedia Commons)
Wire Gauze
- A wire gauze is a rigid, flat piece of square metal mesh.
- A wire gauzes is placed on top of a tripod to hold flat-bottomed glassware while heating with a Bunsen burner.
- In addition to supporting objects over a Bunsen burner, the meshed metal structure allows for the heat of the flame to be spread out more evenly.
- The centre section of a wire gauze will often glow red-hot when in use.
- Since the centre section of a wire gauze gets very hot during use, the safest way to handle them is by the edges, as these should not get hot if the gauze is used correctly.
- Ideally, a wire gauze should be allowed to cool down before being handled.

A wire gauze set up on a tripod, with a beaker and Bunsen burner.
(Image: NagayaS, Wikimedia Commons)
Retort Stand, Bosshead and Clamp
- Retort stands, bossheads and clamps are separate pieces of equipment, but are usually used together.
- They are used for holding certain pieces of glassware and other scientific equipment during experiments.
- A retort stand is a large, upright metal rod attached to a large, flat metal base.
- A bosshead is a device containing two screw clamps, aligned at right angles to each other.
- A clamp as an adjustable gripping device.
- When used together, the bosshead attaches the clamp to the retort stand, while the clamp holds the object being used.
- The screw attaching the bosshead to the retort stand can be used for adjusting the vertical position of the object being held.
- The screw attaching the clamp to the bosshead can be used for adjusting the horizontal position of the object being held.
- Only adjust one bosshead screw at a time, and always support the object while making adjustments to the bosshead.

A retort stand, bosshead and clamp
(Image: Tsaenmai, Wikimedia Commons)
Evaporating Dish
- An evaporating dish is a porcelain dish with a small pouring spout.
- Evaporating dishes are used for evaporating liquids, usually water, from mixtures.
- This can be for the purpose of crystallising solids from solutions (by evaporating all of the water) or for making solutions more concentrated (by evaporating some of the water).
- The evaporation process is usually aided by heating the evaporating dish over a Bunsen burner flame.
- Evaporating dishes come in a variety of sizes, but are usually fairly small.

Evaporating dishes
(Image: Simon A. Eugster, Wikimedia Commons)
Crucible
- A crucible is a small, cup-shaped porcelain vessel with a lid.
- Crucibles are used for heating chemical substances (usually solids) to very high temperatures.
- They are usually heated over a Bunsen burner flame, where they are held inside a pipeclay triangle placed on a tripod.

A crucible with lid
(Image: Good Science)
Pipeclay Triangle
- A pipeclay triangle (also called an clay triangle) is a triangular metal wire frame surrounded by clay or ceramic tubing.
- Pipeclay triangles are placed on tripods to support crucibles or similar objects while they are heated over a Bunsen burner flame.

A pipeclay triangle
(Image: Good Science)
Test Tube Holder
- A test tube holder can take the form of a large wooden peg or special metal tongs with a widened gripping end.
- Test tube holders are usually used when heating test tubes over a Bunsen burner flame.
- The wooden peg type has a more secure grip, but caution needs to be taken so that it doesn’t catch fire when placed near the Bunsen flame.
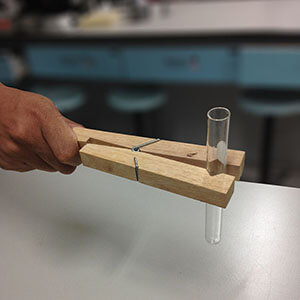

Test tube holders
(Images: Nacharee.jung, Wikimedia Commons; Amitchell125, Wikimedia Commons)
Metal Tongs
- Laboratory metal tongs (also called crucible tongs) are scissor-like metal tongs with a flattened gripping surface.
- They are used for gripping hot objects and for holding solid objects, such as magnesium ribbon, while they are heated over a Bunsen burner flame.
- The rounded mid-sections of the arms are specifically designed for holding crucibles.
- Metal tongs are not suitable for holding test tubes or other glassware as they do not grip them securely enough.

Metal tongs
(Image: Lilly_M, Wikimedia Commons)
Transfer Pipette
- A transfer pipette (also called a plastic pipette) is a disposable plastic device, shaped like a straw, with a sealed round bulb at one end and a narrow opening at the other.
- Transfer pipettes are used for transferring small amounts of liquid.
- The bulb is first squeezed, then the narrow end of the pipette is placed in the liquid. Then, by releasing the squeeze on the bulb, liquid can be taken up by the pipette. The pipette is then taken out of the liquid and transferred by squeezing the bulb again.
- If used gently, transfer pipettes can dispense liquids one drop at a time.

Transfer pipettes
(Image: Lilly_M, Wikimedia Commons)
Safety Mat
- A safety mat (also called a heatproof mat or bench mat) is a hard, heat-proof mat that is placed on a lab bench to protect it from hot objects and chemical spills.
- A heat mat should always be placed under a Bunsen burner or when putting any hot object on the bench.

A well-used safety mat
(Image: Good Science)

