DNA – The Molecule of Life
7 Topics | 6 Quizzes
Chromosomes, Diploid Cells and Haploid Cells
7 Topics | 6 Quizzes
Cell Division – DNA Replication, Mitosis and Meiosis
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
Genes, Genotype and Phenotype
7 Topics | 6 Quizzes
Dominance, Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
4 Topics | 3 Quizzes
Sex-Linked Inheritance
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
Punnett Squares
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
Mendelian Genetics
6 Topics | 5 Quizzes
Pedigree Charts
10 Topics | 9 Quizzes
Genetic Mutation
6 Topics | 5 Quizzes
Genetic Variation and Change
8 Topics | 7 Quizzes
Evolution – The Process
9 Topics | 8 Quizzes
Evolution – The Evidence
6 Topics | 5 Quizzes
3 | DNA Molecules

3 | DNA Molecules
DNA Molecules
- DNA molecules consist of nucleotides that are joined in two ways – firstly, to form a single strand of DNA, and secondly, to form a double strand of DNA.
Single-Stranded DNA
- Single-stranded DNA is formed when nucleotides are joined by a type of covalent bond known as a phosphodiester bond.
- These bonds form between the sugars and phosphates of adjacent nucleotides, creating what is referred to as the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA.
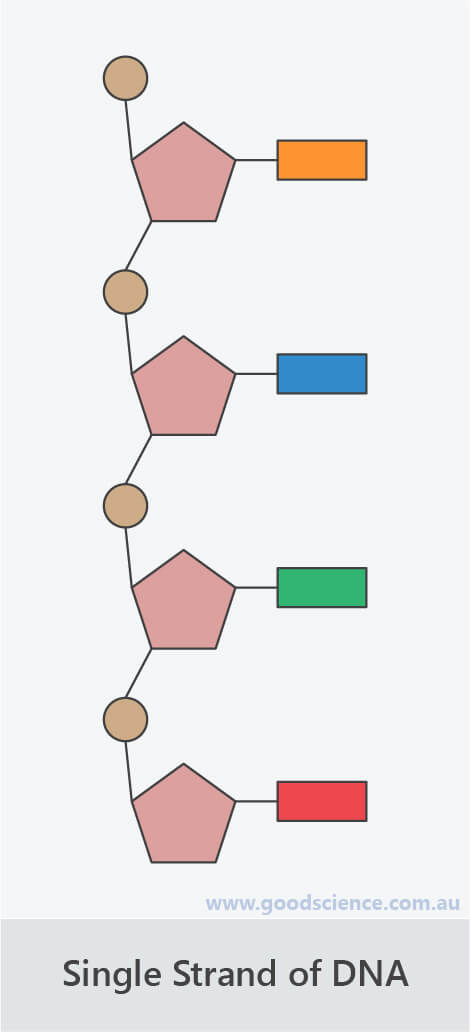
Single strands of DNA are formed by covalent bonds between sugars and phosphates of adjacent nucleotides.
Double-Stranded DNA
- Double-stranded DNA is formed when nucleotides are joined by a type of bond called a hydrogen bond.
- These bonds form between the bases of nucleotides on each strand.
- The two strands are aligned in opposite directions, which is referred to as antiparallel orientation.
- Hydrogen bonds are not full chemical bonds, but are formed due to electrostatic attraction between slightly positive and slightly negative regions of DNA. Therefore, hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds, which allows the two strands of DNA to separate during processes such as DNA replication and gene expression.
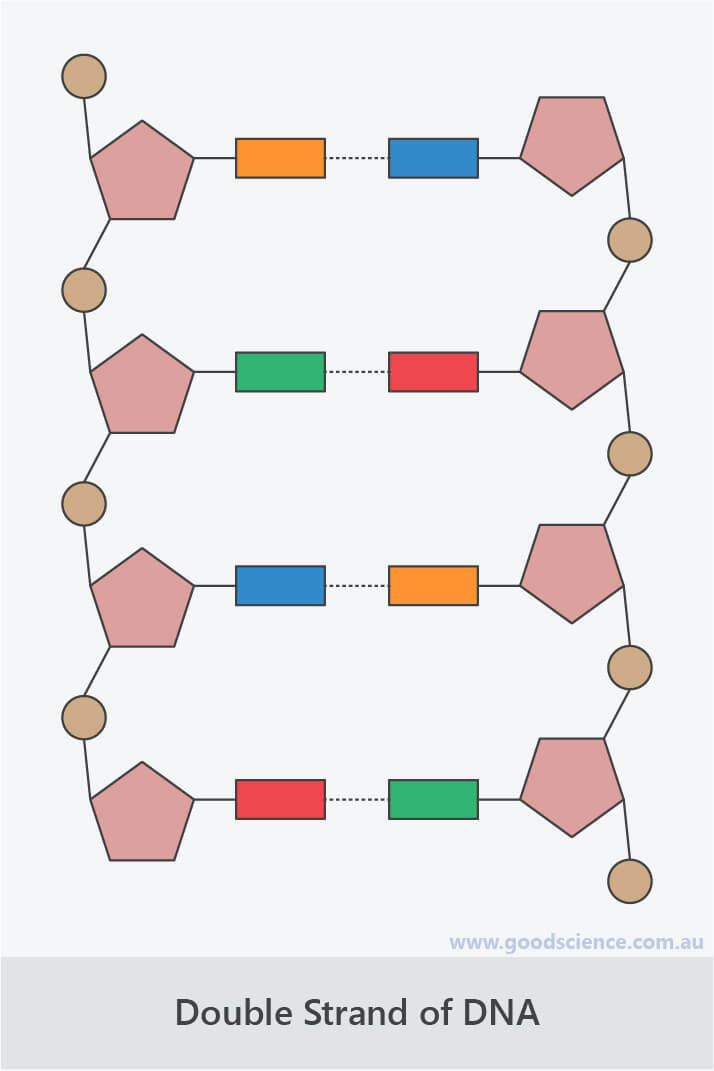
Double strands of DNA are formed by hydrogen bonds between bases of opposite nucleotides.
Quizzes
